| Model: | Dimension: | Input Voltage: | Power: | Beam Angle: | CCT: | CRI: | LED Type: | IP Grade: | Material: | Luminous Efficiency: | Warranty: |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | KD-FLN-W50 | 310mm x 87mm x 170mm | AC 85V - 277V | 50 Watt | 15° / 30° / 45° / 60° / 90° | 3000K / 4500K /6000K | 80 | LED SMD 3030 ( Lumileds ) | IP66 | Aluminium + PC Lens | 130 Lumens per watt | 5 Years |
 | KD-FLN-W100 | 310mm x 87mm x 228mm | AC 85V - 277V | 100 Watt | 15° / 30° / 45° / 60° / 90° | 3000K / 4500K /6000K | 80 | LED SMD 3030 ( Lumileds ) | IP66 | Aluminium + PC Lens | 130 Lumens per watt | 5 Years |
 | KD-FLN-W150 | 310mm x 87mm x 309mm | AC 85V - 277V | 150 Watt | 15° / 30° / 45° / 60° / 90° | 3000K / 4500K /6000K | 80 | LED SMD 3030 ( Lumileds ) | IP66 | Aluminium + PC Lens | 130 Lumens per watt | 5 Years |
 | KD-FLN-W200 | 310mm x 87mm x 382mm | AC 85V - 277V | 200 Watt | 15° / 30° / 45° / 60° / 90° | 3000K / 4500K /6000K | 80 | LED SMD 3030 ( Lumileds ) | IP66 | Aluminium + PC Lens | 130 Lumens per watt | 5 Years |
 | KD-FLN-W250 | 310mm x 87mm x 459mm | AC 85V - 277V | 250 Watt | 15° / 30° / 45° / 60° / 90° | 3000K / 4500K /6000K | 80 | LED SMD 3030 ( Lumileds ) | IP66 | Aluminium + PC Lens | 130 Lumens per watt | 5 Years |
 | KD-FLN-W300 | 310mm x 87mm x 539mm | AC 85V - 277V | 300 Watt | 15° / 30° / 45° / 60° / 90° | 3000K / 4500K /6000K | 80 | LED SMD 3030 ( Lumileds ) | IP66 | Aluminium + PC Lens | 130 Lumens per watt | 5 Years |
 | KD-FLN-W400 | 571mm x 107mm x 388mm | AC 85V - 277V | 400 Watt | 15° / 30° / 45° / 60° / 90° | 3000K / 4500K /6000K | 80 | LED SMD 3030 ( Lumileds ) | IP66 | Aluminium + PC Lens | 130 Lumens per watt | 5 Years |
 | KD-FLN-W500 | 571mm x 107mm x 461mm | AC 85V - 277V | 500 Watt | 15° / 30° / 45° / 60° / 90° | 3000K / 4500K /6000K | 80 | LED SMD 3030 ( Lumileds ) | IP66 | Aluminium + PC Lens | 130 Lumens per watt | 5 Years |
 | KD-FLN-W600 | 571mm x 107mm x 529mm | AC 85V - 277V | 600 Watt | 15° / 30° / 45° / 60° / 90° | 3000K / 4500K /6000K | 80 | LED SMD 3030 ( Lumileds ) | IP66 | Aluminium + PC Lens | 130 Lumens per watt | 5 Years |
 | KD-FLM-W750 | 462mm x 584mm x 111mm | AC 85V - 277V | 750 Watt | 10° / 25° / 45° / 60° / 90° / 65 x 25° / 130 x 30° | 3000K / 4500K /6000K | 80 | LED SMD 3030 ( Lumileds ) | IP66 | Aluminium + PC Lens | 130 Lumens per watt | 5 Years |
 | KD-FLM-W1000 | 462mm x 761mm x 111mm | AC 85V - 277V | 1000 Watt | 10° / 25° / 45° / 60° / 90° / 65 x 25° / 130 x 30° | 3000K / 4500K /6000K | 80 | LED SMD 3030 ( Lumileds ) | IP66 | Aluminium + PC Lens | 130 Lumens per watt | 5 Years |
 | KD-FLM-W1250 | 502mm x 1072mm x 307mm | AC 85V - 277V | 1250 Watt | 10° / 25° / 45° / 60° / 90° / 65 x 25° / 130 x 30° | 3000K / 4500K /6000K | 80 | LED SMD 3030 ( Lumileds ) | IP66 | Aluminium + PC Lens | 130 Lumens per watt | 5 Years |
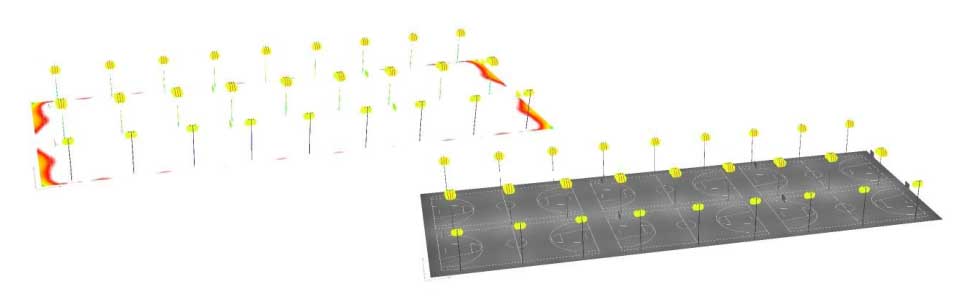
Project 01 ( In the outdoor basketball court ):
Number of Courts: 6
Number of Columns: 27
Column Height: 8 meters
Products Used: 108 piece x 150 watt high power LED flood lights
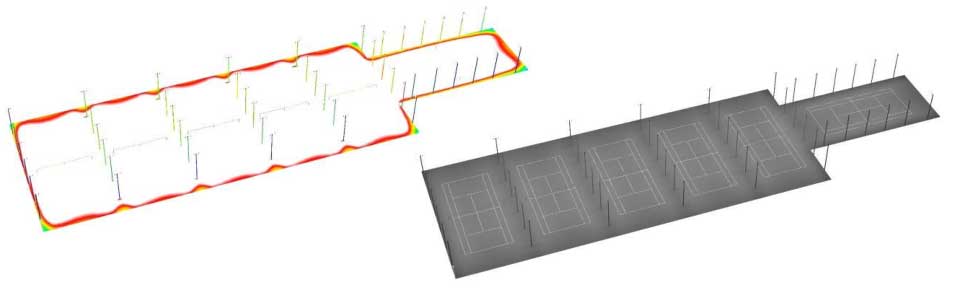
Average illumination:
451 Lux ( Total area );
451 Lux ( basketball court 1 );
451 Lux ( basketball court 2 );
476 Lux ( basketball court 3 );
473 Lux ( basketball court 4 );
453 Lux ( basketball court 5 );
450 Lux ( basketball court 6 );
The calculation report: high power LED flood lights 150 watt x 108 piece ( Project 01 )
Project 02 ( In the outdoor tennis court ):
Number of Courts: 6
Number of Columns: 60
Column Height: 8 meters
Products Used: 120 piece x 150 watt high power LED flood lights
Average illumination:
311 Lux ( Total area );
412 Lux ( tennis court 1 );
443 Lux ( tennis court 2 );
442 Lux ( tennis court 3 );
407 Lux ( tennis court 4 );
403 Lux ( tennis court 5 );
406 Lux ( tennis court 6 );
The calculation report: high power LED flood lights 150 watt x 120 piece ( Project 02 )
Project 03 ( In the outdoor tennis court ):
Number of Courts: 6
Number of Columns: 48
Column Height: 8 meters
Products Used: 72 piece x 250 watt high power LED flood lights
Average illumination:
447 Lux ( Total area );
506 Lux ( tennis court 1 );
528 Lux ( tennis court 2 );
533 Lux ( tennis court 3 );
529 Lux ( tennis court 4 );
525 Lux ( tennis court 5 );
496 Lux ( tennis court 6 );
The calculation report: high power LED flood lights 250 watt x 72 piece ( Project 03 )
| Where can high power LED flood lights be used? | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
The high power LED flood lights are designed to provide a large number of lumens for area, roadway, task or accent lighting. It provide versatile solutions for many industrial and commercial lighting applications such as high pole lighting, parking lot lighting, recreational sports lighting, architectural wall washing and facade lighting.
This versatile line of outdoor luminaires can find a range of applications that require directional lighting within a defined area, whether it is illuminating a point of interest with a strong focused beam of light, or uniformly illuminating a large area or vertical surface with intense white light.
These luminaires can be used as a raised light source to illuminate specific geometric areas such as parking lots, airports, cargo terminals, highway interchanges, sports fields, golf courses, toll plazas, industrial sites and outdoor storage areas.
High power LED floodlights are also used to accentuate and highlight architectural elements such as facades, monuments, columns and iconic structures.
Floodlights are targetable and, combined with proper beam design, placement and mounting height, contribute to very effective and flexible outdoor lighting.
One of the most versatile luminaires, high power LED flood lights are highly coveted for their wide range of applications, high quality light distribution, maintenance free operation and remarkable energy efficiency.
From high pole and high bay lighting to architectural wall washing, facade lighting, stadium and sports field lighting, LED flood lights continue to push the benchmark, providing the best combination of energy efficient vertical and horizontal lighting with superior performance, long-term reliability and significant energy savings.
Combining superior performance with forward-thinking sustainability, this type of lighting offers a complete lighting solution to simplify complex design challenges that traditional metal halide solutions cannot overcome.
Disadvantages of conventional lighting
In the past, high lumen output floodlighting applications were dominated by metal halide lamps. While metal halide lamps last 20 times longer than incandescent lamps, are four times more efficient, and have high wattage (up to 2000 watts), they can also pose some problems.
These lamps operate at higher temperatures (900 to 1100°C) and high pressures (520 to 3100 kPa). At the end of their service life, they are subject to non-passive failure, which may cause a fire hazard.
While lower wattage bulbs may last up to 20000 hours, higher wattage bulbs, such as the 1500 watt bulbs commonly found in stadium fixtures, typically have a dramatically shorter bulb life in the 3000 hour range.
Long start-up and hot restart times, as well as shortened life spans under frequent switching operations, prevent metal halide systems from realizing the energy-saving potential of lighting controls.
Another problem with using metal halide floodlights is the high optical loss. Metal halide lamps throw their lumen output in all directions, which results in low light extraction efficiency.
High wattage luminaires typically require large and complex optics to capture and distribute light, which not only increases the cost and size of the luminaire, but also adds wind load and weight.
In addition to the limited life (about 3000 hours) and poor lumen retention for high wattage applications, metal halide lamps contain large amounts of mercury, which can easily create an explosion hazard.
Industrial and outdoor lighting applications requiring high intensity lighting have previously used so-called high intensity discharge (HID) lamps, including but not limited to metal halide (MH), mercury vapor (HgV), high pressure sodium (HPS), and low pressure sodium (LPS).
Although high wattage (e.g., 1000 watts or more) HID flood lights can produce large amounts of light, their inherent drawbacks limit their use in outdoor lighting applications.
For example, HPS lamps have a large spectrum, but are less efficient (ratio of light delivered to light produced) and less depictive than other light sources.
Advantages of LED lighting
LEDs are an instant-start light source, which will eliminate the initial wait time for HID lamps to start and restart. The solid-state nature of LEDs provides greater resistance to mechanical shock or vibration, which greatly improves their durability.
LED lights are fully dimmable and have no color change. A specific level of light can be obtained by varying the brightness or the operation of the LED lamp.
In addition, metal halide bulbs produce large amounts of short-wave ultraviolet (UV) light, which is dangerous to humans. In contrast, LED lamps emit almost no UV light and have no infrared radiation. LEDs do not contain mercury or any other harmful substances and are therefore environmentally friendly.
Design and configuration of high power LED flood light
High power LED flood lights are complex systems because their thermal, optical and electrical operation is interdependent. A group of system components must work together to form an integrated whole to ensure that the LEDs perform to their full capability under optimally controlled conditions of the operating environment.
In order to provide mechanical strength, thermal management, optical control, power supply and environmental protection, the system into which the LED package is assembled has a significant impact on unlocking the full performance potential of the LED and the value of the luminaire for a particular application.
A high power LED floodlight is either a fully integrated system or a modular component. A fully integrated LED floodlight has a single light engine and the other components are designed specifically to serve the needs of the light engine.
A modular LED floodlight is made up of several LED modules. These modules are independent light engines and include all functional components in addition to the drive circuit.
The modular design offers a high degree of flexibility in the configuration of the luminaire, as well as system scalability for building higher wattage LED floodlights.
Light source
In current LED technology for floodlighting, white light is produced by phosphor-converted LEDs, which combine an InGaN-based blue LED with a phosphor down-converter.
The phosphor-converted LEDs are packaged using different technology platforms, which results in different performance characteristics based on construction materials, package structures and manufacturing processes.
The LED performance characteristics associated with the use of different packaging platforms are most affected by luminous efficacy, lumen depreciation and chromaticity point stability.
Thermal management
High power LED flood light fixtures typically include a housing and electrical (driver) compartment, usually made of low copper die-cast aluminum. Heavy-duty aluminum flood light housings are designed to accommodate all electrical and optical components.
A metal core printed circuit board (MCPCB) provides the thermal connection between the heat sink and the LED package, electrical insulation and power transfer to the LED. The lens frame holds a clear or prismatic lens made of tempered glass or impact resistant polycarbonate.
The frame is then mechanically sealed with a silicone gasket for all-weather operation.
One challenge in designing high power LED lighting fixtures is that high power LEDs emit a lot of heat. Therefore, it may be advantageous to remove the heat generated by the LEDs from the LED semiconductor junction and to keep the internal temperature of the luminaire assembly below the maximum operating temperature so that the electrical and electronic components therein maintain maximum performance.
Therefore, thermal management has become increasingly important in high-power LED lighting. LED flood lights have a cast aluminum heat sink behind the LED assembly to control heat buildup and dissipation.
A heat sink is a heat transfer pathway that is integrated into the lighting system to remove or redistribute heat from the LED through heat transfer with these heat sources. The aerodynamic vents formed by the heat sink fins create efficient air flow and accelerate natural convection. The hot air converges smoothly into a rapid laminar flow that quickly transfers heat to the surrounding environment.
Other thermal management strategies utilize heat pipes that combine the principles of heat conduction and phase change heat transfer mechanisms. The electrical chamber is completely separated from the LED assembly, keeping the driver and other control circuitry very cool, effectively maintaining the life of the driver at high ambient operating temperatures.
The housing is pre-treated and powder coated to withstand extreme weather conditions without cracking or peeling, and to provide optimal color and gloss retention. Flood light designs are increasingly incorporating more aesthetic elements. The attractive, modern design features smooth curves and contoured edges that blend unobtrusively with the environment.
LED driver
A key part of determining the life and performance of high power LED floodlights is the driver. While linear power supplies bring attractive cost and complexity reductions, most LED drivers used to operate high power LED systems are designed as switching power supplies.
The relatively high costs associated with such LED drivers are greatly offset by the drivers’ ability to provide more efficient power conversion, higher quality output and greater protection of the LEDs from abnormal operating conditions.
In addition to the main AC-DC power conversion, SMPS LED drivers perform a number of sub-tasks in sequence or in parallel.
These sub-tasks include harmonic reduction and power factor correction, electromagnetic interference (EMI) screening and filtering, galvanic isolation between primary and secondary, drive current regulation, dimming control, protection against overvoltage, short-circuit, overload and over-temperature faults.
Light distribution
High power LED floodlights are usually direct lighting systems that distribute all the emitted light in the general direction of the illuminated surface. These lamps have symmetrical and asymmetrical beam patterns, with light distribution ranging from narrow spots to wide floods.
The light distribution of a targetable luminaire is usually described in terms of beam spread based on the number of field angles of the luminaire.
The beam spread is usually classified into NEMA beam types from 1 to 7, with tighter beams having lower beam type numbers and wider beams having higher numbers.
The directional nature of LEDs eliminates the need for secondary optics in some area and floodlighting applications. However, most applications require the use of specialised optics to regulate the luminous flux of the light source into a controlled beam.
Optical control of LED floodlights is usually accomplished by means of a reflector or lens. As LEDs provide an opportunity to extract the luminous flux directly from the light source, secondary optics are often designed as packaged scale optics.
A very common design for floodlight optics is to utilise total internal reflection (TIR).
TIR optics produce smooth, circular beams with angular widths as narrow as 10° at full width at half (FWHM) and optical efficiencies of up to 92%.
The challenge of adapting to the environment
Outdoor luminaires are continuously exposed to harsh environmental and extreme weather conditions. Strict control of the environmental conditions of high power LED floodlights is as important as thermal management, optical engineering and drive current regulation.
Integral sealing at all entrances to the luminaire and at material transitions is a necessary practice to protect the lighting system from dust ingress and rain/water from any direction.
Optical components should be protected by toughened glass lenses, which also facilitate the shedding of dust.
During changing environmental conditions or temperature changes within the lighting system, pressure (putting pressure on the seals) and condensation (clouding the lens) can build up within the sealed optical housing.
The installation of a membrane vent in the sealed housing allows the pressure to be balanced and the condensation to be removed.
A chemical conversion coating and a protective powder coating provide corrosion resistance to the aluminium housing.
The construction of the luminaire should have good resistance to mechanical shocks, such as shock and vibration.
Economic Benefit
Economy plays an important role in industrial and commercial lighting applications. Energy consumption, resource conservation, maintenance and long-term sustainability are important factors to consider in any lighting installation. High output lighting systems require a significant amount of electrical energy to produce light for high intensity wide area lighting.
The economic benefits of LED lighting are clear, as it improves efficiency, extends service life, negligible maintenance investment, and greatly reduces the cost of the bulb, thereby shortening the payback time.
Color render index ( CRI )
Solid-state lighting is very favorable in terms of high color rendering lighting, resulting in color rendering index (CRI) values between 70 and 95. CRI is a measure of the quality of color reproduction in artificial lighting products. A higher CRI means better quality, i.e., more natural artificial lighting and easier to detect color discrimination (i.e., perceived nuances of hue).
High CRI in some lighting applications, such as sports lighting, is highly desired for televised sporting events. The excellent color rendering capabilities of LED lighting allow viewers to see the activity on the court with vibrant, bright colors that can distinguish objects even with subtle color differences.
On the other hand, LED lighting produces a beam pattern that can be more easily varied and controlled to meet specifications for light quantity and uniformity, and is therefore useful and desirable in the lighting industry.
Ingress Protection (IP protection class)
Where economically feasible, the LED optics of high power LED flood lights should be sealed with a high IP rating, such as IP65 or above, to prevent the ingress of moisture and contaminants, such as dust, dirt and other particles.
The IP protection class system was drafted by IEC to classify electrical appliances according to their dust and moisture-proof characteristics.
The IP protection level is composed of two numbers, the first number indicates the level of dustproofing of the appliance and prevention of foreign objects (the foreign objects referred to here include tools, human fingers, etc. cannot touch the electrically charged parts of the appliance to avoid electric shock), the second number indicates the degree of sealing of the appliance against moisture and water immersion, the larger the number, the higher the protection level.